Which is More Effective?
Antidepressants and cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) are two of the most common treatments for depression. While both are effective in reducing symptoms, there is debate among mental health professionals about which is better. Some argue that antidepressants provide faster relief and are more effective in severe cases, while others believe that CBT is a more long-lasting and sustainable solution.
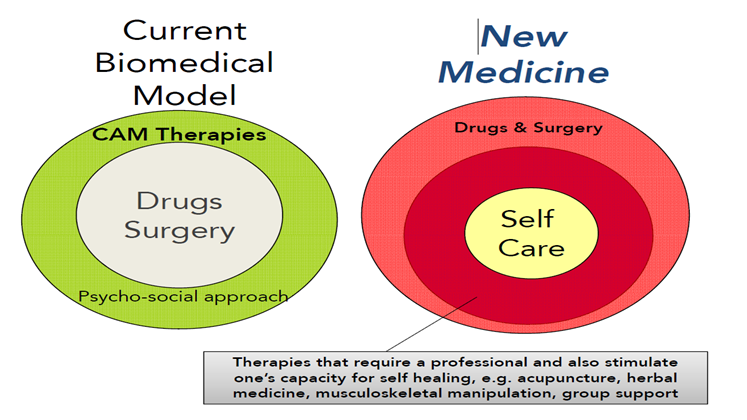
Here in my Cognetive behavioural therapy Dublin clinic I have always been on the side of self care. When it comes to mental health I always favour descriptive (selfcare) over prescriptive (medicines). Research of over 2,000 twins separated at birth from the Minnesota Twin Registry shows that 50% of life satisfaction is attributable to genetics, 40% is attributable to intentional activities (what you think, do and feel) and 10% is due to external events that happen. So we know that if we practice CBT and introduce positive psychology into our lives we can change our lives in a much more positive way, without having to resort to drugs. For me antidrepressants mainly help people from not been depressed or sick, but people want much more than not to be sick they want to thrive and be happy. I will now give you more information on both CBT and antidrepesents so you can have more understanding of both.
Antidepressants are medications that work by altering the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain. They are often prescribed to people with moderate to severe depression and can provide rapid relief of symptoms. However, they come with a range of potential side effects, including nausea, weight gain, and sexual dysfunction. Additionally, some people may not respond well to antidepressants or may experience a relapse of symptoms after discontinuing use.
CBT, on the other hand, is a type of talk therapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviours. It is often used in conjunction with medication, but can also be used as a standalone treatment. CBT is effective in reducing symptoms of depression, and has the added benefit of teaching patients skills to manage their symptoms in the long term. However, it can be time-consuming and may not provide immediate relief for those in crisis.
Understanding Depression
Depression is a mood disorder that can affect a person’s daily life. It is characterized by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in once enjoyable activities. Depression can cause a person to experience feelings of guilt and worthlessness, and they may ruminate on negative thoughts.
Depression is a common mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and life events.
While it is normal for people to feel sad or down from time to time, depression is different. It is a persistent feeling of sadness that lasts for weeks, months, or even years. It can interfere with a person’s ability to function in their daily life, affecting their work, relationships, and overall well-being.
There are several different types of depression, including major depressive disorder, persistent depressive disorder, and bipolar disorder. Each type of depression has its own set of symptoms and treatment options.
It is important to seek help if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of depression. Treatment options include medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of both. It is important to work with a mental health professional to determine the best course of treatment for each individual.
Therapies for Depression
Depression is a common mental health condition that can affect anyone at any age. There are several therapies available to treat depression, including psychotherapy, cognitive therapy, cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy, and behavioural activation.
Psychotherapy is a talking therapy that helps people with depression to identify and understand their negative thoughts and feelings. This therapy can be done one-on-one with a therapist or in a group setting. Cognitive therapy is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns that contribute to depression.
CBT is a form of psychotherapy that combines cognitive therapy and behavioural therapy. This therapy helps people with depression to change their negative thought patterns and behaviours that contribute to their depression. CBT is a highly effective treatment for depression and is as effective as medication in treating mild to moderate depression.
Interpersonal therapy is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on improving relationships with others. This therapy is particularly helpful for people with depression who have difficulty with personal relationships.
Behavioural activation is a therapy that focuses on increasing positive activities in a person’s life. This therapy helps people with depression to identify and engage in activities that they enjoy and that give them a sense of purpose.
Talking therapies, such as counselling, are also effective treatments for depression. Counselling helps people with depression to talk about their feelings and emotions in a safe and supportive environment.
Self-help strategies, such as exercise, mindfulness meditation, and relaxation techniques, can also be effective in treating depression. These strategies can be used in combination with other therapies or as a standalone treatment.
In conclusion, there are several therapies available to treat depression. Each therapy has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best treatment option will depend on the individual’s needs and preferences.
Antidepressant Medications
Antidepressant medications are a common treatment for depression and other mood disorders. They work by altering the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. There are several types of antidepressants, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), and second-generation antidepressants.
SSRIs, such as sertraline and fluoxetine (Prozac), are the most commonly prescribed antidepressants. They are generally well-tolerated and have fewer side effects than other antidepressants. SNRIs, such as venlafaxine and duloxetine, work by blocking the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. They are also effective in treating depression and anxiety disorders.
TCAs, such as amitriptyline and imipramine, were some of the first antidepressants developed. They work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. However, they have more side effects than SSRIs and SNRIs, including dry mouth, constipation, and blurred vision. MAOIs, such as phenelzine, are used less frequently due to their potential interactions with certain foods and medications.
Second-generation antidepressants, such as escitalopram and mirtazapine, are newer medications that have been developed to be more selective in their actions on neurotransmitters. They are generally well-tolerated and have fewer side effects than TCAs and MAOIs.
It is important to note that antidepressants may not work for everyone and may take several weeks to start working. They should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional and should not be stopped abruptly. Additionally, there is a risk of side effects, including nausea, headaches, and sexual dysfunction. It is important to discuss any concerns or questions with a healthcare professional before starting an antidepressant medication.
Side Effects and Risks of Antidepressants
Antidepressants are a commonly prescribed medication for individuals experiencing depression and other mental health disorders. While they can be effective in treating symptoms, they also come with potential side effects and risks that should be carefully considered.
One potential side effect of antidepressants is the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviour, particularly in children and young adults. It is important for individuals taking antidepressants to be closely monitored for any changes in mood or behaviour and to report any concerns to their healthcare provider immediately.
Other potential side effects of antidepressants include constipation, drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, and diarrhea. These side effects can vary depending on the specific medication and individual and may go away over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
It is also important to note that abruptly stopping antidepressant medication can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and irritability. It is recommended that individuals work closely with their healthcare provider to slowly taper off medication when discontinuing use.
Overall, while antidepressants can be an effective treatment option for individuals experiencing depression and other mental health disorders, it is important to carefully consider the potential side effects and risks before starting medication. Close monitoring and communication with a healthcare provider can help ensure safe and effective use of antidepressants.
CBT vs Antidepressants
When it comes to treating depression, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and antidepressants are two common options. Both have been shown to be effective in treating depression, but they work in different ways.
Antidepressants, such as Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), are medications that work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin. This can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Antidepressants are often used as a first-line treatment for moderate to severe depression.
CBT, on the other hand, is a type of talk therapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviours that contribute to depression. It is often used as a standalone treatment for mild to moderate depression, but can also be used in combination with antidepressants for more severe cases.
Studies have shown that both CBT and antidepressants can be effective in treating depression. In fact, a combination of the two may be even more effective than either treatment alone.
One study found that a combination of CBT and antidepressants led to higher rates of response and remission compared to either treatment alone. Another study found that the combination treatment was more effective at preventing relapse than either treatment alone.
However, it is important to note that not everyone responds to or tolerates antidepressants. Some people may experience side effects, such as nausea, insomnia, or sexual dysfunction. Additionally, there is a risk of relapse once treatment is discontinued.
CBT, on the other hand, is generally well-tolerated and has few side effects. It can also be a more sustainable long-term treatment option, as it teaches individuals skills to manage their depression on their own.
Overall, the choice between CBT and antidepressants will depend on the individual and their specific needs and preferences. It is important for individuals to work with their healthcare provider to determine the best treatment approach for their depression.
Role of Exercise and Lifestyle Changes
While antidepressants and CBT therapy are both effective treatments for depression, exercise and lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing symptoms. Exercise has been shown to boost mood, reduce stress, and improve self-esteem, making it a valuable addition to any treatment plan.
Regular physical activity can help reduce symptoms of depression by increasing the production of endorphins, the body’s natural “feel-good” chemicals. Exercise can also provide a sense of accomplishment and help individuals feel more in control of their lives, which can improve self-esteem.
In addition to exercise, lifestyle changes can also be beneficial for managing depression. Stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help reduce feelings of anxiety and improve overall well-being. Eating a healthy diet and getting enough sleep are also important factors in maintaining good mental health.
While exercise and lifestyle changes can be helpful, it is important to note that they should not be used as a substitute for professional treatment. Individuals with depression should work with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that includes a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Advanced and Alternative Treatments
While antidepressants and CBT therapy are the most commonly used treatments for depression, other advanced and alternative treatments may be effective for some individuals.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a treatment that involves inducing a seizure in the brain using electrical currents. It is typically used for individuals who have not responded to other treatments, including antidepressants and psychotherapy. ECT is generally considered safe and effective, although it may cause some side effects such as confusion and memory loss.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a treatment that involves implanting a device in the chest that sends electrical signals to the vagus nerve, which runs from the brain to the abdomen. The device is typically used for individuals who have not responded to other treatments, including antidepressants and psychotherapy. VNS is generally considered safe and effective, although it may cause some side effects such as hoarseness and coughing.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a treatment that involves using a magnetic field to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. It is typically used for individuals who have not responded to other treatments, including antidepressants and psychotherapy. TMS is generally considered safe and effective, although it may cause some side effects such as headache and scalp discomfort.
Ketamine
Ketamine is a medication that is typically used as an anaesthetic. However, it has also been shown to have rapid antidepressant effects in some individuals. Ketamine is typically administered intravenously in a clinical setting, and its use for depression is still being studied.
Overall, while these advanced and alternative treatments may be effective for some individuals, they are typically reserved for those who have not responded to other treatments. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment approach for each individual case.
Depression in Primary Care
Depression is a common mental health disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is often treated in primary care settings, where general practitioners (GPs) play a crucial role in identifying and managing the condition. According to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), primary care practitioners should be able to recognize depression and offer treatment options such as medication or psychological therapies.
In primary care settings, antidepressants are commonly prescribed to treat depression. They are effective in reducing depressive symptoms and are beneficial for individuals with moderate to severe depression. However, there are concerns about the over-prescription of antidepressants, which can lead to adverse effects and the development of drug dependence.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is another treatment option for depression. It is a psychological therapy that aims to change negative patterns of thinking and behaviour. According to a study conducted by Vanderbilt University, CBT was found to be effective in treating depression, with similar efficacy to antidepressants.
Despite the effectiveness of both antidepressants and CBT, there is no clear consensus on which treatment option is better. The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s preferences and the severity of their depression. In some cases, a combination of both treatments may be recommended.
In conclusion, depression is a common mental health disorder that is often treated in primary care settings. Antidepressants and CBT are both effective treatment options, and the choice of treatment depends on individual factors. GPs play a crucial role in identifying and managing depression, and it is important to consider the risks and benefits of each treatment option before making a decision.
Research and Studies on Depression Treatments
Depression is a complex and multifaceted disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. There are various treatment options available for depression, including antidepressants and cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT). This section will discuss the research and studies conducted on these two treatment options.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are medications that are commonly used to treat depression. There have been several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and meta-analyses conducted on the efficacy of antidepressants for depression treatment. A systematic review of 522 RCTs found that antidepressants were more effective than placebo in treating depression symptoms (Cipriani et al., 2018). Another meta-analysis of 522 RCTs found that antidepressants were more effective than placebo in treating moderate to severe depression (Cipriani et al., 2018). However, the effect size of antidepressants was found to be small (Cipriani et al., 2018).
The Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD) is a widely used tool to measure the severity of depression symptoms. A meta-analysis of 117 RCTs found that antidepressants were more effective than placebo in reducing HRSD scores (Eyding et al., 2010). However, the effect size of antidepressants was found to be small to moderate (Eyding et al., 2010).
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
CBT is a form of talk therapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviours that contribute to depression. Several RCTs and meta-analyses have been conducted on the efficacy of CBT for depression treatment. A meta-analysis of 23 RCTs found that CBT was more effective than control conditions in reducing depression symptoms (Cuijpers et al., 2016). Another meta-analysis of 45 RCTs found that CBT was as effective as antidepressants in treating depression (Amick et al., 2015).
My Conclusion:
So, both antidepressants and CBT have been shown to be effective in treating depression. Antidepressants have a small to moderate effect size, while CBT has a moderate effect size. The choice of treatment should be based on individual patient needs and preferences.
However, there is no clear answer as to which one is better.
Antidepressants can be effective in reducing symptoms quickly, but they come with potential side effects and may not work for everyone. CBT therapy is a more long-term solution that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviours, but it requires a significant time commitment and may not be accessible to everyone.
Ultimately, the decision to use antidepressants or CBT therapy should be based on individual factors such as the severity of the depression, personal preferences, and the advice of a healthcare professional. It may also be beneficial to consider a combination of both treatments for optimal results.
Overall, it is important to remember that depression is a complex and individualized condition, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach to treatment. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to find the best treatment plan for each individual. For more information on CBT and positive psychology contact me here https://flowpsychology.ie/



